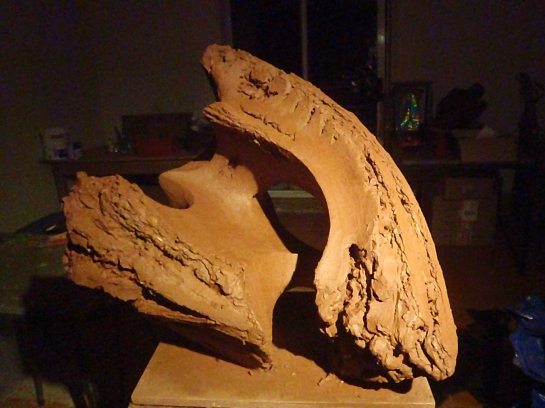
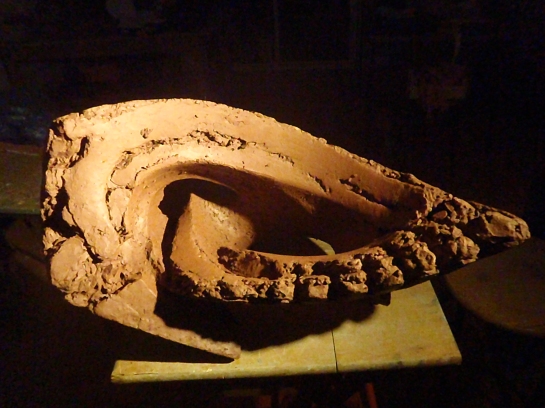
There are lots of variations on the Coil-Building method. This one avoids all the pit-falls that cause your pots to go out of shape or break in the kiln.
I started out as a Coil-builder 34 years ago and I still turn to it regularly. All my monumental brick sculptures are coil-built. It’s all about understanding the clay and how joins are actually formed. The skills you gain from coil-building are extremely transferable making it a great place to start for beginners. There is a lovely rhythm to the work.
Here is the Coil-building Workshop that I run at Osprey Studios. Many thanks to my lovely students for being in these pictures.
How to do excellent Coil-Building.
Choose a clay with a medium to high percentage of multi-grade grog ( grit in different sizes from dust to medium sized bits). Scarva ES 50 Crank is ideal. Clays of this type will give you the best results.

1.Start with the biggest pinch-pot you can comfortably make. (Unless your piece is really too big; leave out as much of the centre of the base as possible.)
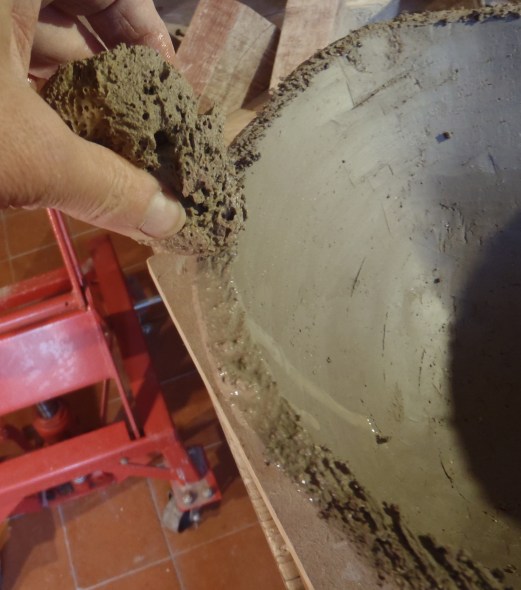

7.Prepare the top edge to make a join. NEVER use a pointy tool. Use a serrated tool so that the score marks are not too deep. Fill these ‘ditches’ with water and give it time to soak in. Dab on a little more. Then put on slip; slip is perfect for holding a lot of water in place.
Very important bit.
Genuine joins are formed when the chains of platelet-shaped particles from each section inter-lock. Imagine a magnified image of tangled hair.
Score marks do not give the surface ‘tooth’; they allow water into the clay-body. On vertical surfaces score marks and slip hold the water in place to give it time to sink in.
Slip is not ‘glue’. It is clay particles spread out in water and has little strength, especially when it has dried. It is ideal for holding a lot of water in place to give it time to be absorbed to soften the area of leather-hard clay.
Never use a needle tool. Your score marks will be too narrow and deep. They will get covered over, resulting in a ring of tiny but malevolent air-bubbles that will expand in the firing and a crack will zing along the joins. I have fired pots for poor, misinformed makers that have come apart at every coil! You could see the deep score marks and powdery slip.

8.Start making your coil from a generous block of clay. Squeeze it gently and repeatedly into a thick sausage shape.

9.Using 2 hands gently, and rotating, squeeze your coil until it is 2 or 3 cm thick. Do NOT roll your coil.
Every join is an opportunity for a crack, every coil a point where you might loose control of your shape. So it makes sense to use coils that are large enough to handle well and will give you 4cms of height.
Rolling your coil on the table can cause 2 problems;
- The grog that would have helped create an excellent join is packed towards the centre of the coil and the finer particles of clay are packed together to form a ‘skin’ of tight platelet shaped particles that are reluctant to reach out and bond with the platelets of the pot.
- enthusiastic rolling often causes a tunnel to form at each end of the coil that would be a substantial, damaging air-bubble. This is why you often see coil-builders break off both tips of their coils with out even looking at them; they know that hazard is probably there.

10.Rub the softened score-marks and excess slip off the pot until the edge is sticky not slippery. Your platelets are raised and receptive.

11.Attach 1 end of your coil. Hold the other end high. Gradually lower the coil, expelling air and any surplus slip.

12.Guide the coil downwards and forwards with a pinch. This action creates a friction between the 2 surfaces that causes the platelets to hook onto each other from the pot to the coil.
Do not be tempted to push clay down the pot with this step. Go to the end of your coil and stop. Do NOT go up another layer!

13.pinch upwards gently only at the seam off the join. (your finger and thumb will touch pot and coil each time) I call this lining-up. Do inside first; this may push the wall out. next do outside; this will correct a bulge.
The over-hang of the coil can trap air if hastily pressed down. Rushed building is why coil-pots have a very unfair reputation for being hideous.

15.With thumbs inside and fingers on outside ( for best control) gently pinch the clay in the desired direction for your shape. Use many light pinches not a few strong ones for best results. The most important thing is the thickness. Not the height.
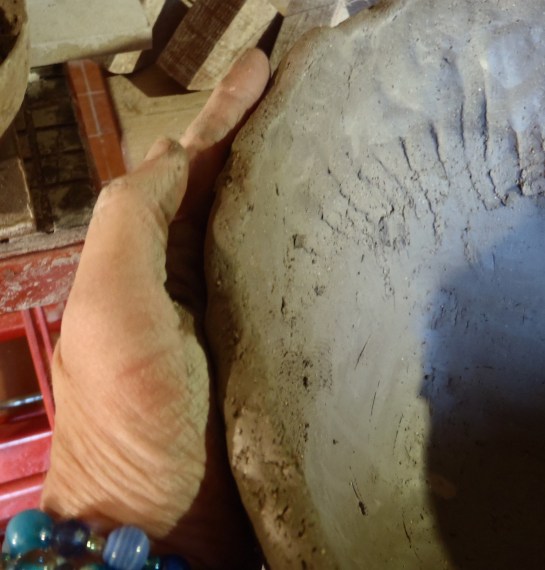

16.Support with 1 hand on outside. Gently move clay in many directions to get that coil right where you want it. Inside first, of course.

18.Support hand on outside, use serrated kidney to improve inner surface. Go in many directions, gently combing the clay into place. Then do the outside.
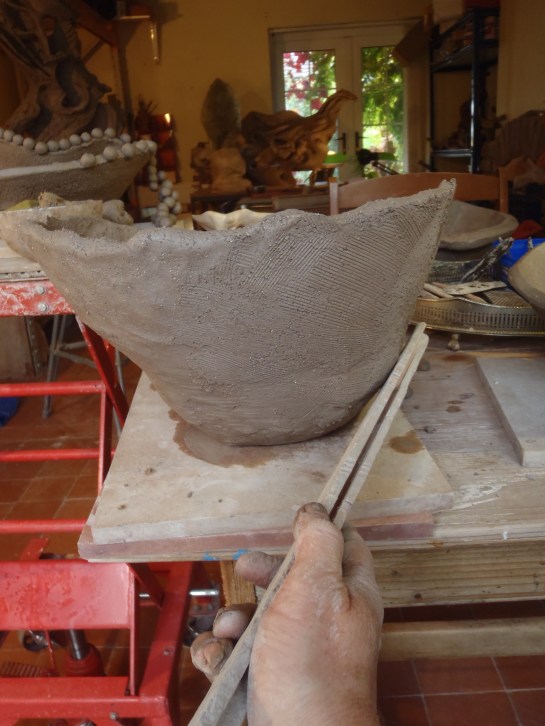

20.Sit back and look at the outline of your form. Use a paddle (flat stick) to tap in bumps or bulges. Rotate around the whole form in stages so that the stress of this action is spread evenly through the clay. Paddling compacts the clay particles making your form very strong. But over-doing it on one area can lead to cracks because it alters the drying rate.

23.Soften any indented areas that you don’t like and add clay to fill them. Add textures in the same way. Paddle them gently.

25.Now even up the top edge by subtracting or adding clay. Let it stiffen. Go over it again with a surform blade.( these take off nice controllable layers.)

26.Spend a lot of time on the edge. use firm tools to compact the clay and get every millimetre of that edge exactly how you want it: attention to this detail will transform your pot. Also tidy up the bottom edge where your form meets the table.
Coils are perfect for all sorts of applications.

28.This bio-morphic head is being built on a clay armature with the techniques described in How to Make a Head. I use coils attached in exactly the same way as I would on a pot to get excellent joins. The coil is then pinched in the direction I want it to go.
Using Supports.
When you are making complicated shapes use temporary supports made of clay that will shrink with the form. Build in support walls and buttresses. Use rigid supports with care: plan to accommodate the shrinkage.

29.Here I am putting down the first layers of 2 big sculptures.
I am using Coleford brick clay in a very soft state. My ‘coils’ are half bag blocks but they are applied and treated in the same way as any good coil.
The walls are thicker at the base to support the considerable weight of the next layers.
The internal support-walls are thinner.
On very big sculptures these support walls will be discarded when the sculpture is cut into sections.
On medium sized sculptures, that will be cut into parts not panels, the internal support walls will be left in to maintain the shapes of the sections during firing.
30.Note the finger marks left by the process: these are just like the marks of a serrated-kidney on a smaller pot. Like corrugation, they add strength to the wet clay wall and will be left on until the clay is firm enough to hold it’s shape.
The same layer of the fired panel-sections of Bruce during installation.

31.Bruce in progress, 3m wide x 2 m high. There is a clay support wall under his head and the stack of blocks was added later and removed as soon as the head was firm enough to cut apart.
Here’s some good examples of rigid supports in action:

32. Mynydd Mawr Courtyard Sculpture, Tumble, Carmarthen, Wales, 2m H x 190cm W. The big blocks are firm memory foam which will accommodate the shrinkage. I often use it inside a piece to support ceilings. It gets removed when the piece is cut up.

33.Because this rigid support leans outwards it will not constrict the shrinkage. It was adjusted repeatedly during the build.

34.Mynydd Mawr, Tumble, nearly complete. Larger sculptures are always built from a scale model. The internal support walls are worked out in advance and the cutting of sections planned so that those walls will support the section’s shape during firing.

35.Balarat Pit Marker,in progress, 6m L x 2m H. ( Ocean Colliery Pit Marker in background.) Memory foam on top of clay support walls inside the sculpture supports that long roof and accommodates the shrinkage.

36.The Sirhowy Wyvern in progress, 3m L x 2 m H. A tunnel runs under the horse with carved images on it’s walls so we needed access to it. A thin support wall blocks the tunnel half way. It supports the structure but allows us to crawl in do the art-work ( a lot was done by some fab children) The support was discarded when we cut the sections. We didn’t get to see the tunnel right through until it was installed on site.

37.Bucket and stool supporting the tunnel roof while we built it. The board to the left of the picture is there to protect some intricate carving about the Sirhowy Iron Works during the build.
Adding clay on to the surface.
38.All the big coiled sculptures have artwork added onto the surface once it is firm. Exactly like the smaller pot, the area is softened using scored ‘ditches’ and slip to hold the water in place, allowing it to soak in to the firm clay and raise up those platelet shaped clay particles ready to join with soft clay.
Once a good join is achieved the added clay is modelled and carved in stages as the clay firms up. The drying ( and shrinking) is kept slow using plastic covers to allow that vulnerable join to set as the water moves from the soft added clay into the firm wall.
Remember that water will always want to be level and will travel down the form over time as well as evaporating from the surface. This passage of water past those platelets completes the join. If there is too much water it will collect and run down the join, destroying the bond.
With that in mind add as much clay as your artwork needs. If it becomes more that 2 cm thick hollow it from the inside even if this means cutting the section out of the form, hollowing it and reassembling it. The important thing is to find a way to get the look you want. For advice on this process click here: Working solid and hollowing sections out.
Drying coil-built forms.
39.Use plastic to shield firm parts from drying while you work on new parts. e.g. a strip of plastic sheet to keep the top edge soft while you put art-work on a lower area before it gets to hard. And visa-versa.
Slow the drying as much as possible to allow all those joins to set using plastic sheets.
Cover the piece in a shield of newspaper ( 5 sheets thick) or a cardboard box or fabric sheets (not wet) to create a damp micro-climate that will slowly release the water from the clay and protect from drafts that would cause un-even drying (and maybe, consequently, cracking)
Related info on this site.
For a full description of how the really big sculptures are done click here: Building Brick Sculptures on a monumental scale.
The whole story of the fab Gwalia Mynydd Mawr Care and Nursing Home Courtyard Sculpture designed with local primary school children and staff and residents of the Home, run by Arts Care Gofal Celf in Carmarthen, Wales: Studio Diary, The Tumble Commission, parts 1-8.
Using clay armatures and coils: How to Make a Head: Clay Armatures and Building Hollow.
Questions?
put your questions in the Comments below and I will do my best to answer them.
If you follow this site you will get an e-mail each time I put up a new post. I hope these ‘How to..’ posts are useful. Pass them on freely. Share pictures of what you make on my Facebook. I would love to see it.